Ceaseless challenge toward the top
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Perfect products can be able to be produced when those elements form a trinity.
Here, we will be discussing about absorption of gypsum mold which is one of essential elements in pottery industry among physical properties of gypsum for making pottery mold.
Plasters used for making pottery mold are called PLASTER OF PARIS in Korea and it was named because it is made by calcine of gypsum produced plentifully in 3rd Paris basin of France.
In Korea, it is called gypsum for making molds.
The main reason why plaster is used as model in pottery industry, forming die for pouring paste or for forming die as a machine is that it has various advantages such as easiness to manufacture, excellent absorptiveness, quick dryness and easiness for mass production of models for its relatively low cost.
Plaster is CaSO4 · 1/2H2O, which is manufactured through calcine of CaSO4 · 2H2O gypsum.
- Gypsum - Molecular weight of CaSO4ㆍ2H2O: 172.18 CaSO4 79.1% H2O 20.9%
- Plaster - Molecular weight of CaSO4ㆍ1/2H2O: 145.15 CaSO4 938. % H2O 6.2%
- Anhydrous gypsum - Molecular weight of CaSO4: 136.15 CaSO4 100%
Plasters are divided into alpha and beta type, and alpha - CaSO4 · 1/2H2O(alpha - hemihydrate gypsum) is manufactured by wet manufacturing method and pressure vapor method and pressure solution eclectic method are also used for manufacturing.
- Beta - CaSO4ㆍ1/2H2O(beta-hemihydrate gypsum) is manufactured by normal pressure calcine which is the dry manufacturing method.
Water absorption ratio of gypsum is referred to as maximum quantity that gypsum mold can absorb water under atmospheric pressure.
Test method is that after manufacturing about 1kg gypsum mold under the condition of 20℃ room temperature and water temperature and calculate with the following formula in 45℃ thermal drying machine.
Water absorption ratio(%) = < (wet weight after absorption - dry weight) / weight > x 100Test Results
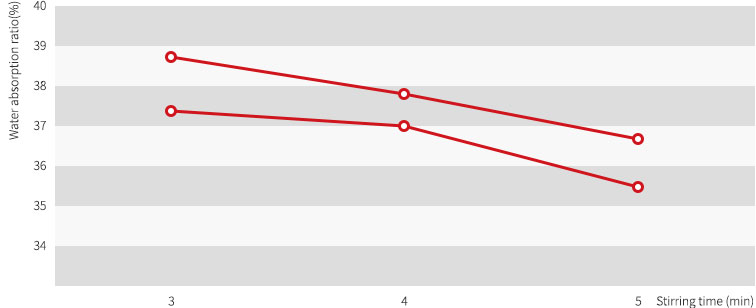
Mixing time and water absorption ratio
Water absorption ratio when setting mixing ratio to 75% and varying stirring time to 3minutes, 4 minutes and 5 minutes for specimen 1Kg after pouring it into a vacuum mixer is same as Table 1 and Figure.
| Stirring speed | Mixing Time | Water absorption ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 300rpm | 3min | 38.5% |
| 300rpm | 4min | 37.6% |
| 300rpm | 5min | 36.5% |
| 450rpm | 3min | 37.7% |
| 450rpm | 4min | 37.1% |
| 450rpm | 5min | 35.4% |
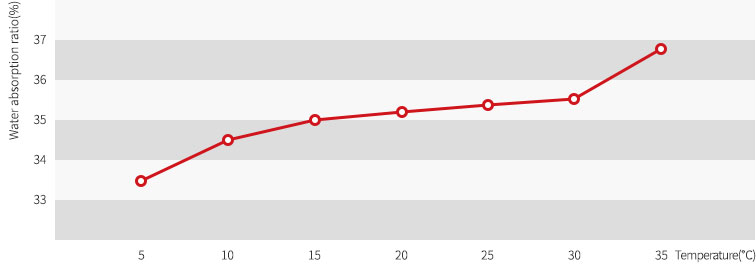
Water temperature and water absorption ratio for making mold
Water absorption ratio when setting mixing ratio to 75% and varying water temperature to 5℃, 10℃, 15℃, 20℃, 25℃, 30℃ and 35℃ is same as Figure.
Condition and water absorption ratio for making gypsum mold
The more the mixing ratio and water absorption ratio, the more the water absorption ratio.
The longer the Mixing time (make sure to stir enough), the less the water absorption ratio.
The lower the water temperature when making a mold, the less the water absorption ratio
Absorption speed of gypsum mold refers to the speed that gypsum mold absorbs water.
As for test method, dry 30×30×110mm prism at 45℃ in advance and have it to absorb only in floor surface, and apply glue to floor surface to be deposited 5mm and measure time until it absorbs water to 50mm high from floor surface.
Also, for expansion speed, find the value of diffusion coefficient Dg with the following formula by measuring the height of water rise every hour with the above specimen.
Dg=(x/)² (㎠ / sec)
X : Height of water rise of water from floor surface(Cm)
t : Time that gypsum prism rose to X cm from the time it contacted with water(Sec)
Condition for making gypsum mold and absorption speed
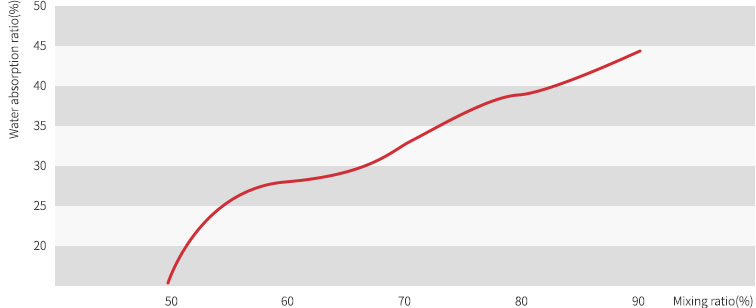
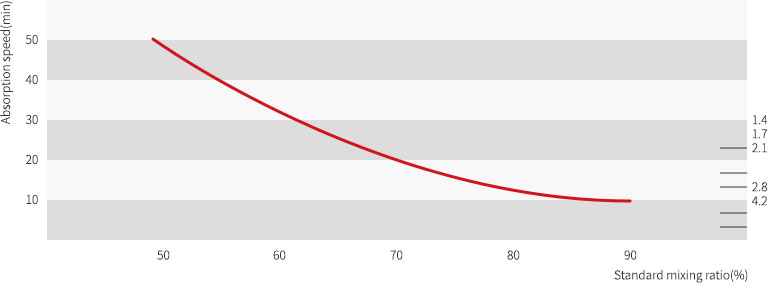
- The lower the mixing ratio, the slower the absorption speed(diffusion coefficient becomes smaller), the higher the mixing ratio, the faster the absorption speed (diffusion coefficient becomes larger).
- The shorter the stirring time, the faster the absorption speed, but the longer the time, the slower the absorption speed.
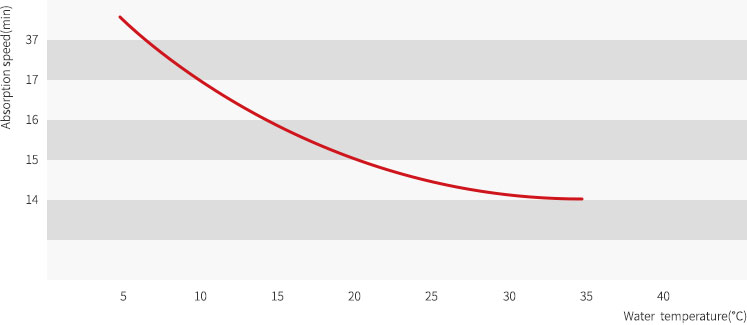
- The lower the water temperature, the slower the absorption speed, but the higher the water temperature, the faster the absorption speed.
Test Results
Standard Mixing Ratio and Absorption Speed – The relation between standard mixing ratio and absorption speed is same as Figure 4.
Mixing time and absorption speed
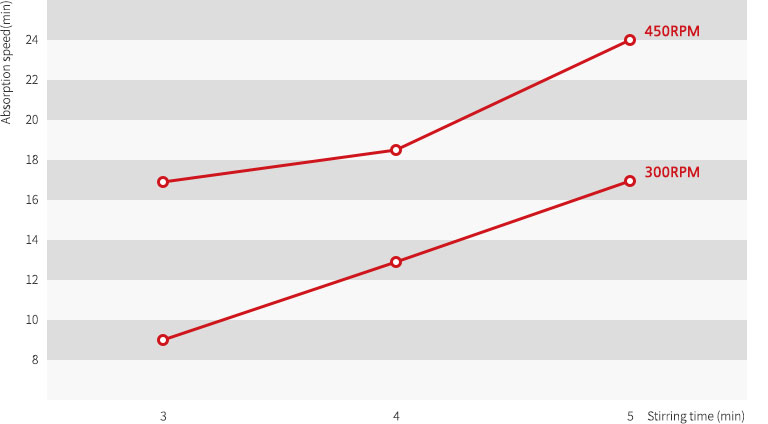
Absorption speed when changing stirring time of specimen 1Kg to 3, 4 and 5 minutes for Mixing speed(300rpm, 450rpm) in vacuum mixer with 75% of mixing ratio is same as Table 2 and Figure 5.
| Stirring speed | min | 교반시간과 흡수율 |
|---|---|---|
| 300rpm | 3min | 8:50 |
| 300rpm | 4min | 13:30 |
| 300rpm | 5min | 17:10 |
| 450rpm | 3min | 16:30 |
| 450rpm | 4min | 18:20 |
| 450rpm | 5min | 24:00 |
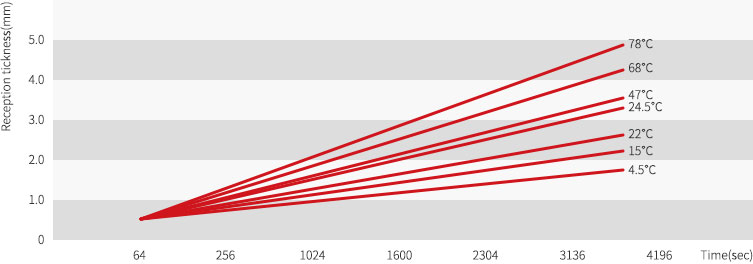
Water temperature & Absorption speed for mold making
Absorption speed when changing water temperature to 5℃~35℃ with 75% of mixing ratio is same as Figure 6.
Absorption power & receptiveness of gypsum mold
Absorption power of gypsum mold refers to the power (quantity) to absorb and receive barbotine.
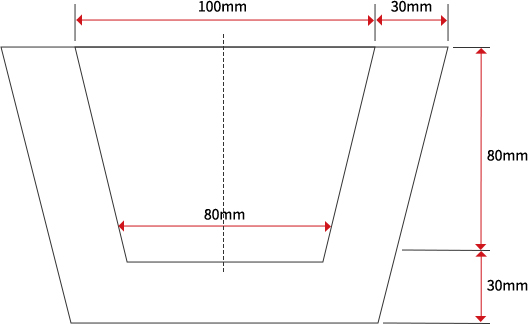
In general, after making and drying a test pattern same as Figure 7, inject barbotine and have it to be received for a certain period of time (Ex. 30minutes) and release molding bodies after having the rest slips run and leave for a certain period of time (Ex. 30minutes) before measuring weight and water of clay bodies.
The less the water in molding bodies, it means that absorption power becomes stronger. Absorption power of gypsum mold differs according to the size of air vent of gypsum mold.
Appendix 1) As shown in the picture of electron microscope, plaster in body of hardening of gypsum dissolves and the crystal of irrigation educes, forming the tissue.
If mixing Ratio is low and stirring much, and water temperature is low, porosity becomes smaller as it becomes dense and air vent becomes smaller, and dense capillaries appear in countless numbers and are pumped up.
Accordingly, moving speed of water of the body of hardening gets slower and absorption power becomes stronger.
Condition and water absorption ratio for making gypsum mold
If mixing ratio is low, absorption power becomes stronger, whereas the power becomes weaker when the ratio is high.
If stirring time is short, absorption power becomes stronger, whereas the power becomes stronger when stirring sufficiently.
If water temperature is low, absorption power becomes stronger but becomes weaker when the temperature is high.
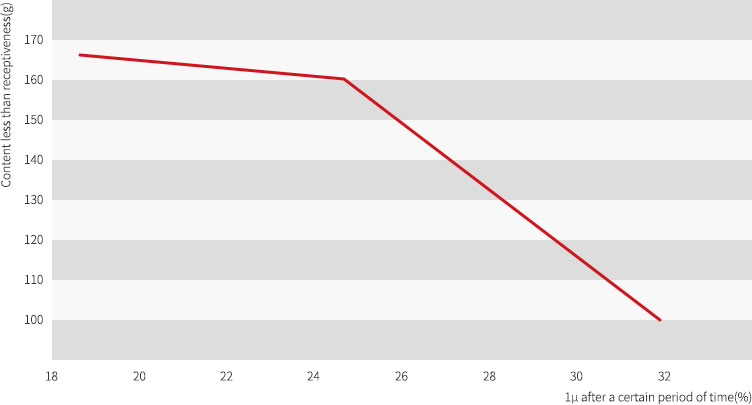
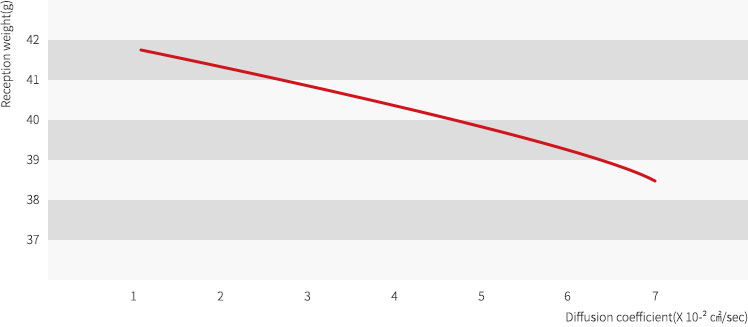
Diffusion coefficient and receptiveness of gypsum mold
If absorption speed is fast, diffusion coefficient becomes larger but becomes smaller when the speed is slow. The relation between diffusion coefficient and receptiveness of gypsum mold is same as Figure 8.
Refer DATA